Cosmos is a decentralized network that aims to solve the scalability and interoperability issues faced by many blockchain networks.
In this beginner’s guide, we will explore what Cosmos is, how it works, and why it is gaining traction in the cryptocurrency world. So, let’s dive in and learn more about this digital currency.
What is Cosmos ?
Cosmos is a blockchain ecosystem, often referred to as the “Internet of Blockchains.” The ecosystem comprises hundreds of different blockchains that are all able to link with each other and easily swap tokens between each other.
All of the blockchains are built on the open-source Cosmos technology, which is made available through a software development kit. This approach minimizes complexity and offers developers the flexibility to add any features they desire. The kit provides common functionalities like staking and governance.
Plus, many of them use the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol, to ensure secure communication between blockchains. This is what enables messages and tokens to be sent between chains.
How does Cosmos work?
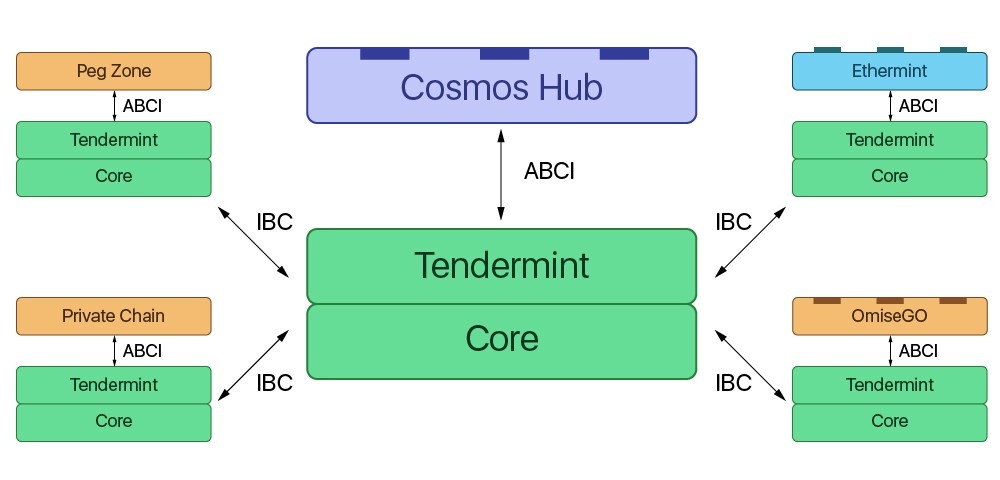
The Cosmos network is an ever-expanding ecosystem of apps and services interconnected.
It uses hubs, the Tendermint consensus algorithm, and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to ensure that blockchains can communicate securely.
Some platforms communicate with each other using smart contracts. Through this process, tokens are locked in on one platform and then the asset’s corresponding amount is minted on the other. The wrapped tokens are a typical example of this process.
Rather than sending Bitcoin from the Bitcoin blockchain to another platform like Ethereum, the BTC gets locked in a functional blockchain that provides the service. The correspondent amount such as wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) is issued in pegged tokens on another blockchain.
In contrast, Cosmos offers open-source tools to allow developers to build decentralized and sovereign blockchain applications called zones instead of relying on one single chain. The zones are Cosmos smart contracts.
The Cosmos team has built the software development kit (SDK) that allows developers to build zones faster, simpler and cheaper than other platforms like Ethereum.
It minimizes complexity by offering the most common functionality among blockchains such as staking, governance and tokens through well-known and simple-to-use software development programs like GO. Developers have the maximum freedom and flexibility to create plugins and add any features they want.
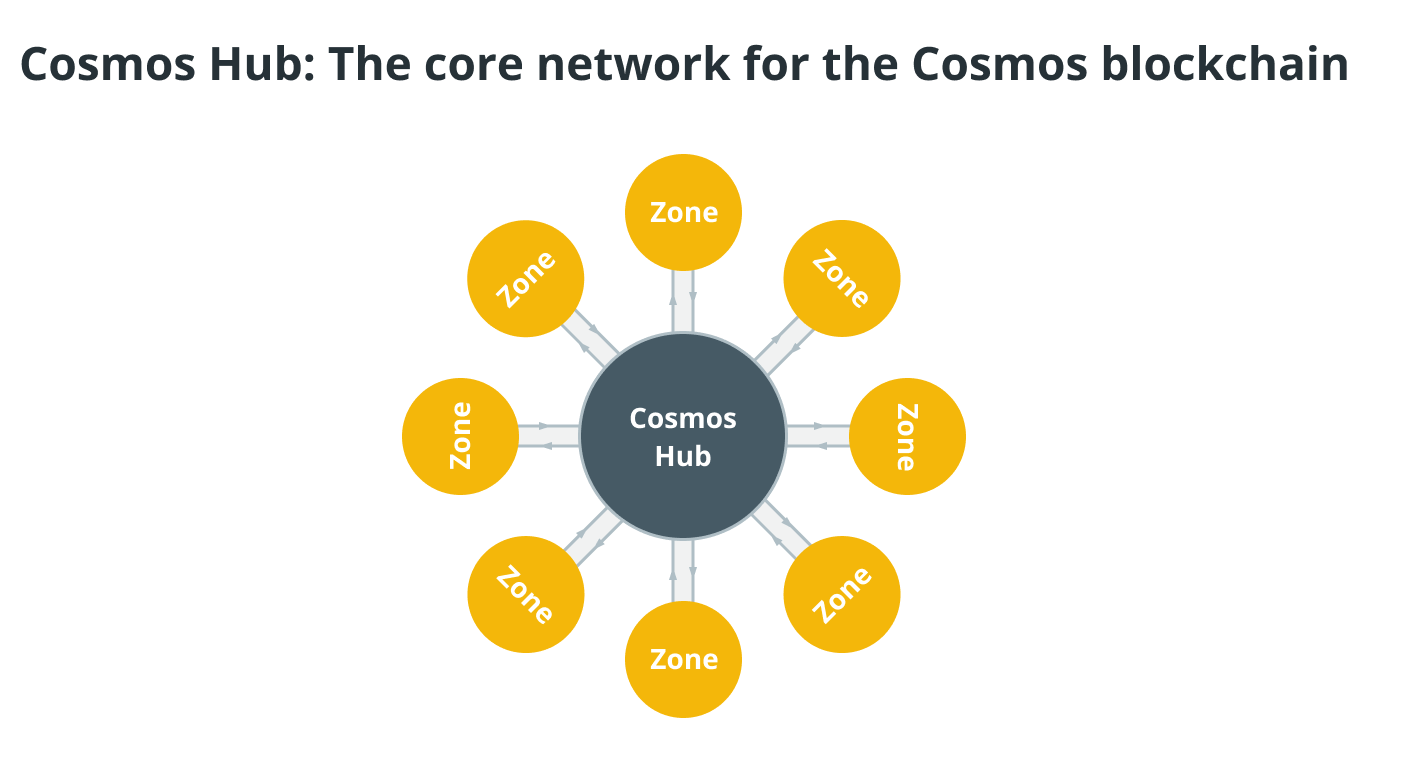
Cosmos Hub: The core network for the Cosmos Blockchain
Delving deeper into the Cosmos ecosystem, the Cosmos Hub holds a unique position.
It serves as the primary hub in the network where each new zone, or decentralized blockchain application, is linked. The Cosmos Hub, the first blockchain launched on the Cosmos network, maintains a record of each zone’s state and vice versa, allowing for seamless interaction and communication between zones. Each zone is autonomous and capable of executing functions such as authenticating accounts and transactions, creating and distributing new tokens, and making blockchain changes.
Many chains in the Cosmos ecosystem are focused on specific use cases. For instance, Osmosis primarily serves as a decentralized exchange — although it has upcoming competition as dYdX launches its own Cosmos-based chain.
The Cosmos Hub also facilitates interoperability with other proof-of-work blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, through bridges. This connectivity extends to blockchains that may not necessarily meet the requirements of the Cosmos protocol.
The native cryptocurrency, ATOM, is instrumental in the Cosmos Hub. Network participants can stake ATOM, earning rewards and potentially becoming validator nodes. Validators power the blockchain and vote on changes. The more ATOM staked, the higher the voting power for the validators. Users can delegate their tokens to validators, promoting honest performance. They can switch between validators, depending on their voting preferences, offering flexibility.
Other blockchains can also draw on Cosmos Hub’s security using a feature called Replicated Security. This allows them to launch without their own set of validators.
IBC: Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol
The Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol is a core feature of the Cosmos ecosystem, developed to facilitate communication, data transfer, and interoperability between independent blockchains. Unlike traditional blockchains that function in isolation, the IBC bridges the connectivity gap by empowering these chains to communicate and exchange messages in a standardized manner.
IBC’s design emphasizes modularity, making it a general-purpose protocol. This means that even blockchains outside the Cosmos ecosystem can implement IBC, granting them interoperability with other IBC-enabled chains. This is particularly impactful in the realm of decentralized finance applications, which often necessitate interactions across several chains.
The structure of the Cosmos network comprises “hubs” and “zones.” Hubs, such as the Cosmos Hub, serve as central blockchains that can interface with multiple zones, which are other individual blockchains. IBC enables the seamless transfer of tokens and data between these zones and hubs. A key advantage is that it leverages the inherent security of the individual blockchains. This ensures the secure exchange of information, with the assurance that the compromise of one chain doesn’t risk the security of the others.
A fundamental component that makes IBC efficient is its utilization of light client verification. When two chains wish to communicate, there’s no need to validate the entire counterpart’s state. Instead, they use light clients, which are streamlined versions of a blockchain node, to authenticate cryptographic proofs tied to transactions on the opposite chain. IBC’s protocol involves the transmission of packets between chains. While it standardizes how these packets are sent and received, it leaves the specifics of their handling to the individual chains, providing them a degree of autonomy and flexibility.
What problem does Cosmos solve?
Cosmos’ objective is to enable communication between all blockchains while solving the three main blockchain problems: sovereignty, scalability and sustainability.
Sovereignty
The Cosmos free SDK allows developers to build sovereign blockchain apps without ongoing costs. These blockchains can easily interconnect without relying on smart contracts to exist on a different blockchain, thereby avoiding high transaction fees due to network congestion while developing better scaling features.
This will boost innovative functionalities in decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, gaming, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), social networks, marketplaces and the economy that relies on the internet, especially the ownership economy in which everyone has a stake.
Scalability
Cosmos interoperability is what guarantees the functioning of a scalable system. By integrating to Cosmos interoperability model of shared communication standards, any type of sovereign blockchain will be able to communicate with each other and contribute to the evolution of its protocol design.
Cosmos scalability can be obtained by duplicating a blockchain to relieve congestion or splitting the apps into multiple application-specific blockchains. Interchain token transfers allow these multiple chains to continue one network.
Sustainability
Sustainability is assured by the PoS consensus algorithm, which secures the network. PoS reduces carbon footprint by 99% compared with the PoW consensus algorithm.
Who is behind Cosmos crypto?
The development of Cosmos is the result of cooperation between different teams. Primary resources and funds for its development were allocated by the Swiss Interchain Foundation (ICF), a non-profit organization that funds and supports open-source blockchain projects, and the Tendermint team.
Software developers Jae Kwon and Ethan Buchman co-founded the Cosmos network in 2014 while also creating Tendermint, the consensus algorithm that would power Cosmos. Kwon and Buchman authored the Cosmos white paper in 2016 and later released its software in 2019.
The Interchain Foundation held the first series of fundraising with a two-week initial coin offering (ICO) of the ATOM token in 2017, accumulating over $17 million.
Tendermint Inc. raised $9 million to continue the development of the project through a Series A funding round in 2019. Jae Kwon left the project in early 2020, pledging he would stay involved anyway, while the other co-founder, Ethan Buchman, is still president of the Interchain Foundation Council.
Cosmos has attracted investment from several prominent names in crypto including Paradigm, Bain Capital and 1confirmation.
The future of the Cosmos blockchain
The road ahead appears encouraging for the Cosmos ecosystem. Significant improvements are expected in terms of security with the development of Interchain Security. This will guarantee better protection across all the interconnected chains.
More fluidity in IBC connections will facilitate DeFi transactions and interchain NFT transfer across different public and permissioned blockchains.
Cosmos’ upcoming plans are ambitious and include many more features, but it has a team of hard-working developers behind it that allows its participants to hope for a promising future.






